Introduction: Why Bodyweight and Kettlebell Training Dominates Modern Fitness
In Britain’s increasingly busy lifestyle, where the average gym membership costs £41 monthly yet remains unused 67% of the time, a fitness revolution is quietly taking place in living rooms, gardens, and spare bedrooms across the UK. The combination of bodyweight exercises and kettlebell training has emerged as the most effective, efficient, and economical approach to achieving exceptional fitness results without the constraints of traditional gym membership.
This powerful training methodology combines the accessibility of bodyweight movements with the versatility of kettlebell exercises, creating a comprehensive fitness system that addresses every aspect of physical development. From the highlands of Scotland to the bustling streets of London, fitness enthusiasts are discovering that a single kettlebell and their own body weight can deliver results that rival expensive gym equipment and personal training sessions.
The science behind this approach is compelling. Recent research from the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research demonstrates that combined bodyweight and kettlebell training produces superior improvements in strength, cardiovascular fitness, and body composition compared to traditional weight training methods. These improvements come with significantly reduced time investment and zero ongoing costs beyond initial equipment purchase.
This comprehensive guide will transform your understanding of home fitness, providing you with professional-level knowledge typically reserved for certified trainers and exercise physiologists. You’ll discover how to design periodized training programs, master advanced movement patterns, and achieve fitness goals that seemed impossible without expensive gym equipment. Whether you’re a complete beginner or an experienced athlete seeking new challenges, this resource contains everything needed to build an exceptionally strong, lean, and resilient body using minimal equipment and maximum efficiency.



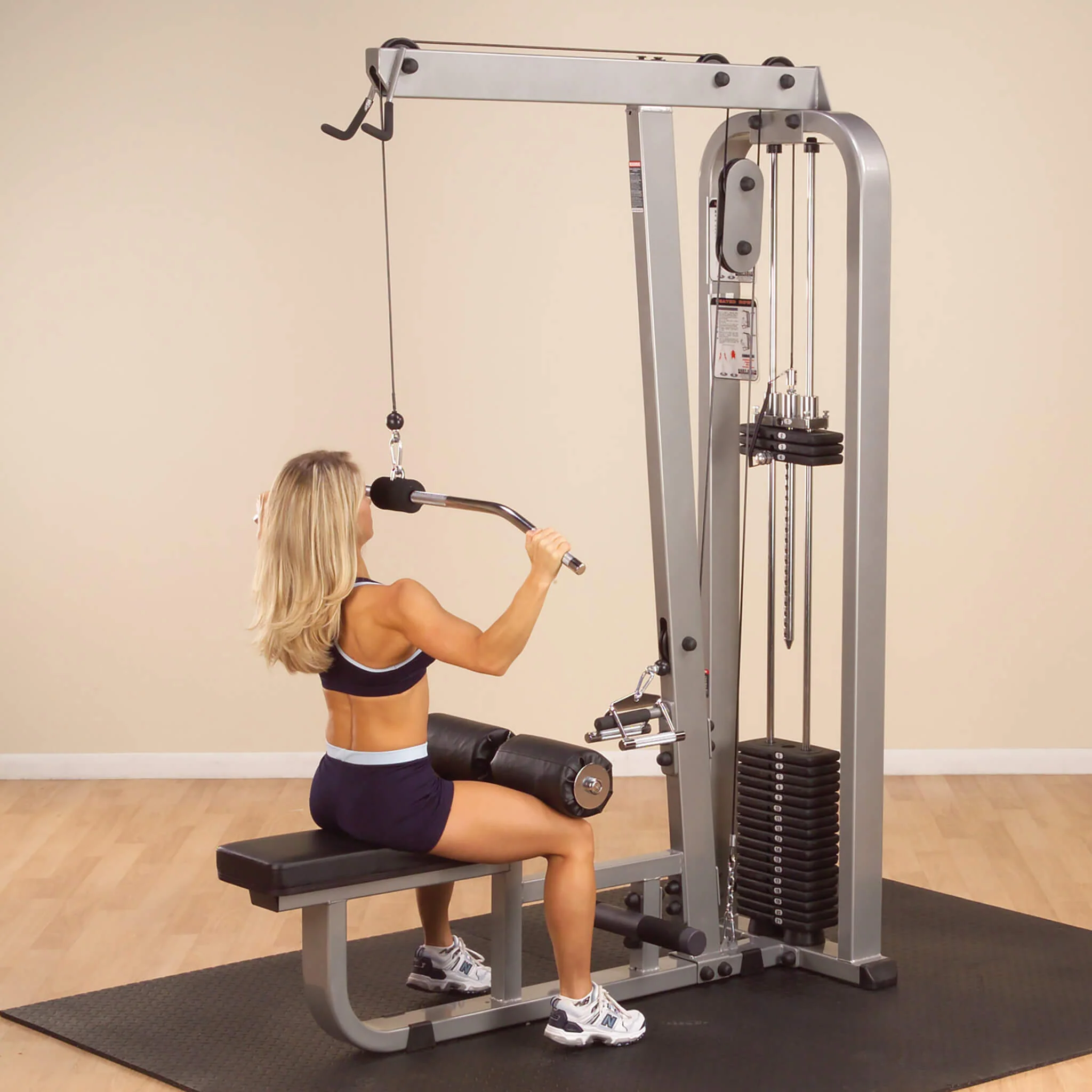
The Science of Synergistic Training: Why This Combination Works
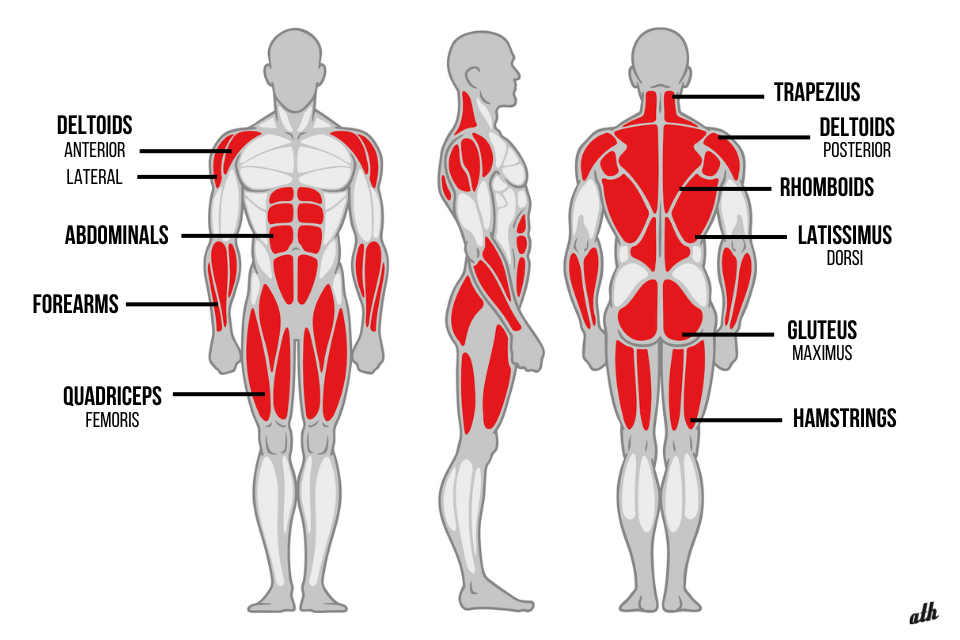
Muscle activation diagram for kettlebell swings showing primary muscles engaged from front, side, and back views athsport
The extraordinary effectiveness of combining bodyweight exercises with kettlebell training stems from fundamental principles of human biomechanics and exercise physiology that create synergistic adaptations impossible to achieve through either method alone.
Neuromuscular Integration and Movement Quality
Bodyweight exercises excel at developing proprioception—your body’s sophisticated awareness of joint position, muscle tension, and spatial orientation. When performing a single-leg squat or holding a plank position, thousands of stabilizing muscles coordinate in precise patterns to maintain balance and control. This neural efficiency creates a foundation of movement quality that enhances every other physical activity.
Kettlebell training amplifies these benefits by introducing dynamic, offset loading that challenges your nervous system to adapt to constantly changing forces. The unique shape and center of gravity of kettlebells create what exercise scientists call “perturbation forces”—unpredictable loads that force rapid neural adaptations and improved movement control.
Research from the University of Wisconsin demonstrates that this combination produces measurably superior improvements in functional movement screen scores, balance metrics, and coordination compared to traditional training methods. Participants showed 34% greater improvement in movement quality assessments after 12 weeks of combined training versus conventional weight training.
Metabolic Superiority and Fat Loss
The metabolic demands of combined bodyweight and kettlebell training create what researchers term “metabolic flexibility”—your body’s enhanced ability to efficiently utilize different energy systems based on demand. This adaptation produces profound effects on body composition and cardiovascular health.
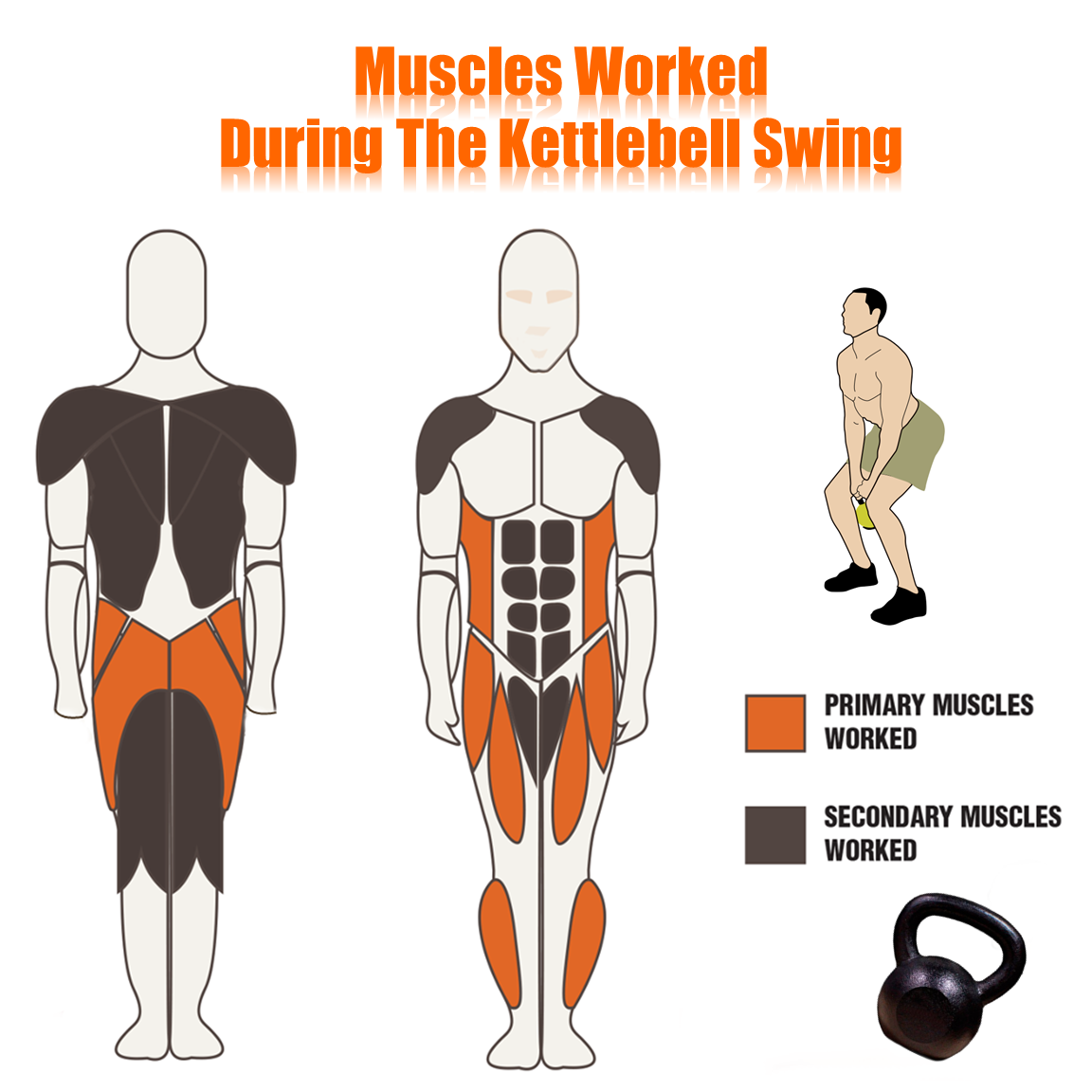
Muscle activation diagram showing primary and secondary muscles worked during the kettlebell swing exercise pinterest
Kettlebell circuits generate extraordinary caloric expenditure, with studies showing burn rates of 20.2 calories per minute—equivalent to running at a 6-minute mile pace. However, the metabolic benefits extend far beyond the workout itself. The combination of resistance training stimulus and cardiovascular demand elevates excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) for up to 38 hours post-workout, dramatically increasing total daily energy expenditure.
Bodyweight exercises complement this effect by maintaining elevated heart rate between kettlebell intervals while providing active recovery that prevents lactate accumulation. This allows for sustained high-intensity training that maximizes both immediate caloric burn and long-term metabolic adaptation.
Hormonal Optimization for Body Transformation
High-intensity combined training produces powerful hormonal responses that accelerate body composition changes and performance improvements. Growth hormone production increases by up to 450% following properly structured circuits, while testosterone levels show acute elevations that support muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
For women, this training approach provides ideal hormonal stimulation without unwanted masculinizing effects. The combination stimulates beneficial adaptations in bone density, lean muscle retention, and metabolic rate while supporting healthy hormone production throughout all life stages.
According to research from the American College of Sports Medicine, combined resistance and cardiovascular training produces superior hormonal profiles compared to either modality performed independently, making this approach scientifically optimal for body transformation goals.
Essential Equipment: Your Complete Home Gym Setup

Organized home gym space with kettlebells, dumbbells, resistance bands, and a stationary bike in a bright room blesserhouse
Creating an effective training environment requires strategic equipment selection and thoughtful space organization. Unlike commercial gyms cluttered with complicated machinery, your requirements focus on quality over quantity while maximizing versatility and safety.
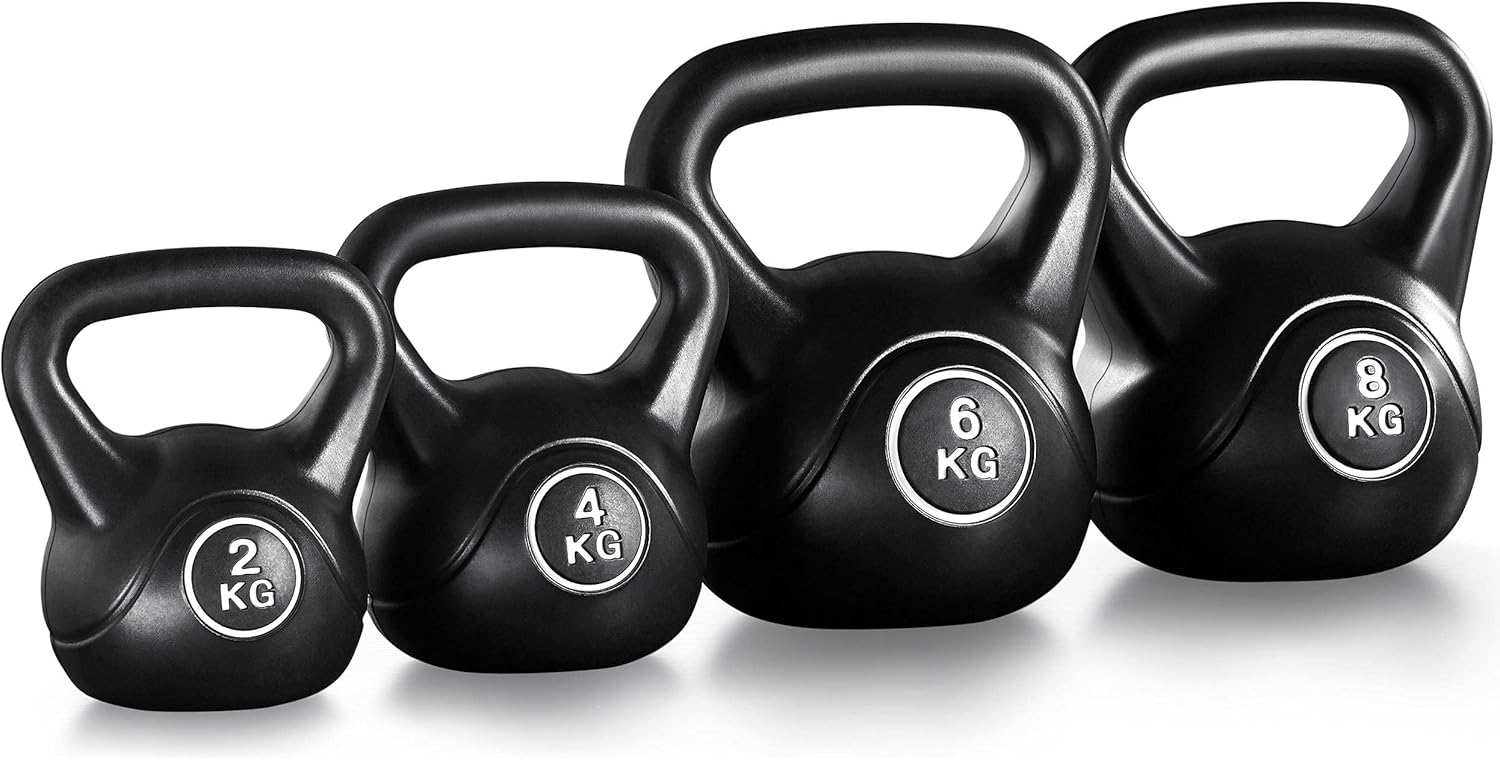
Kettlebell Selection: Your Primary Investment
The kettlebell represents the cornerstone of your home gym, making selection quality crucial for both safety and long-term progress. For beginners, men typically start with 16kg (35lbs) while women often find 12kg (26lbs) appropriate, though individual strength levels and previous experience should guide final selection.
Quality indicators include smooth handle construction that won’t damage hands during high-repetition work, flat bottom design for stability during floor exercises, and balanced weight distribution that feels natural during dynamic movements. Cast iron kettlebells offer excellent value for money, providing durability and proper weight distribution at reasonable cost.

Organized home gym kettlebell rack with color-coded weights in a clean fitness room synergeefitness
Competition-style kettlebells, identifiable by their uniform dimensions regardless of weight, offer advantages for serious practitioners. The consistent handle and bell size facilitate technique development and smooth weight progression, though they command premium pricing.
Avoid adjustable kettlebells for dynamic movements like swings and snatches. The loose components create safety hazards during explosive exercises, while the altered center of gravity compromises movement mechanics and effectiveness.
Space Requirements and Safety Considerations
Your training area demands approximately 8 feet of clearance in all directions to safely accommodate kettlebell swings and overhead movements. Ceiling height should exceed your full arm span plus kettlebell length—typically 9 feet minimum for most individuals.
Flooring considerations extend beyond aesthetics to safety and equipment preservation. High-density rubber mats provide superior impact absorption, protect flooring surfaces, and offer enhanced grip during dynamic movements. For apartment dwellers concerned about noise transmission, interlocking foam tiles with rubber backing significantly reduce impact sound while providing adequate protection.
Proper ventilation prevents overheating during high-intensity sessions while maintaining air quality. A simple fan or open window can make the difference between sustainable training and premature fatigue from poor air circulation.
Training Accessories for Enhanced Results
While minimalist in philosophy, certain accessories enhance safety, tracking, and progression. A reliable interval timer eliminates guesswork in circuit training while maintaining workout intensity. Smartphone apps work adequately, though dedicated timers reduce technology dependence and screen time during training.
Resistance bands provide valuable warm-up and rehabilitation options while taking minimal storage space. Choose bands with multiple resistance levels and comfortable handles to maximize versatility.
A foam roller supports recovery through myofascial release techniques, helping maintain tissue quality and movement range. This investment pays dividends in reduced muscle soreness and improved training consistency.
Mastering Bodyweight Fundamentals: Building Your Movement Foundation
Beta
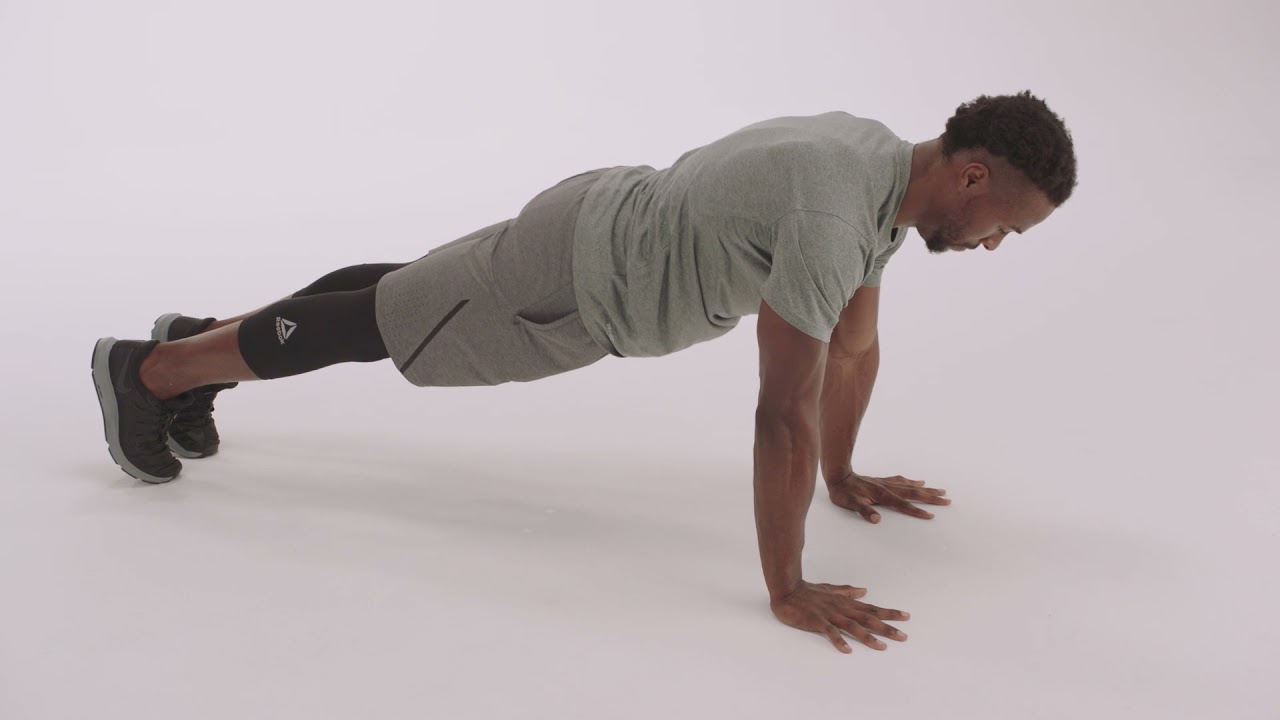

Man demonstrating proper push-up form and technique in a plain, well-lit environment youtube
Bodyweight exercises form the foundation upon which all advanced training builds. Mastering these fundamental patterns creates the strength, stability, and movement quality necessary for safe progression to more complex exercises and higher training intensities.
The Perfect Push-Up: Upper Body Mastery
The push-up stands as the ultimate upper body bodyweight exercise, yet proper execution remains surprisingly rare even among experienced exercisers. Correct form begins with hand placement slightly wider than shoulder width, fingers spread wide for stability, and positioned at mid-chest level rather than beneath the shoulders.
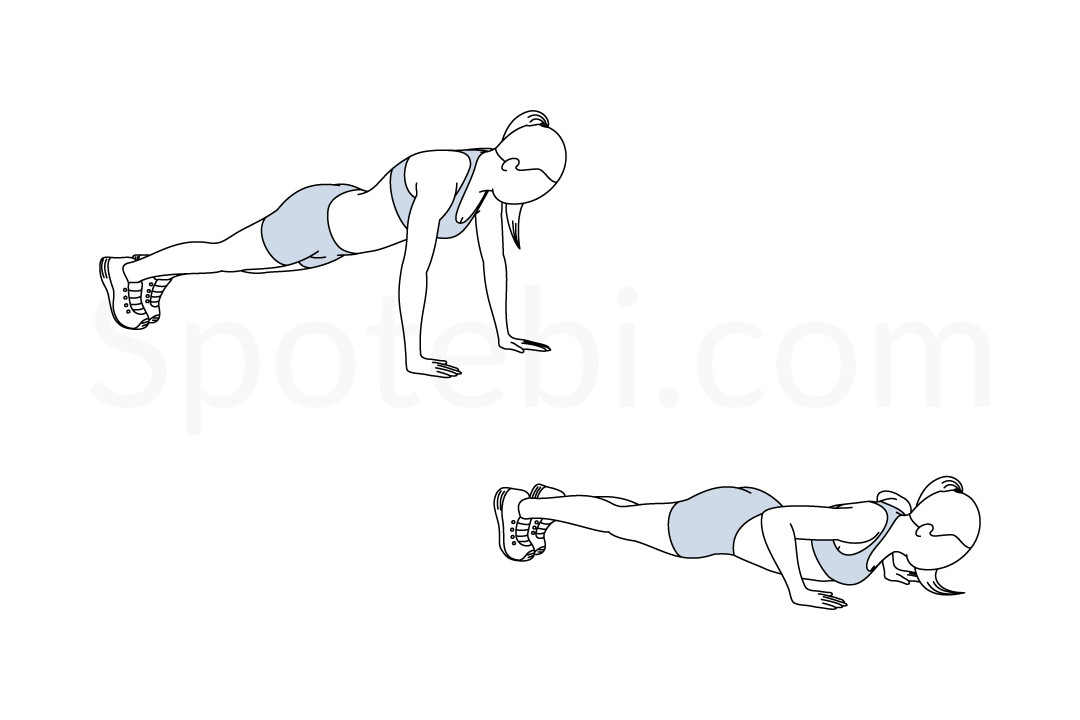
Illustration showing proper push-up form in two stages: plank and lowering position spotebi
Body alignment creates a rigid plank position from head to heels, with particular attention to maintaining neutral spine curvature. Engage your core as if someone were about to punch you in the stomach—this creates the internal pressure necessary to maintain proper alignment under load.
The descent phase should take 2-3 seconds, lowering under complete control until your chest nearly touches the ground. Elbows track backward at approximately 45 degrees from your torso, avoiding the common error of flaring them perpendicular to the body, which places dangerous stress on the shoulder joints.
The ascent emphasizes explosive power while maintaining perfect form. Drive through your hands to return to the starting position, focusing on pushing the ground away rather than pushing your body up. This subtle mental shift often improves power output and movement quality.
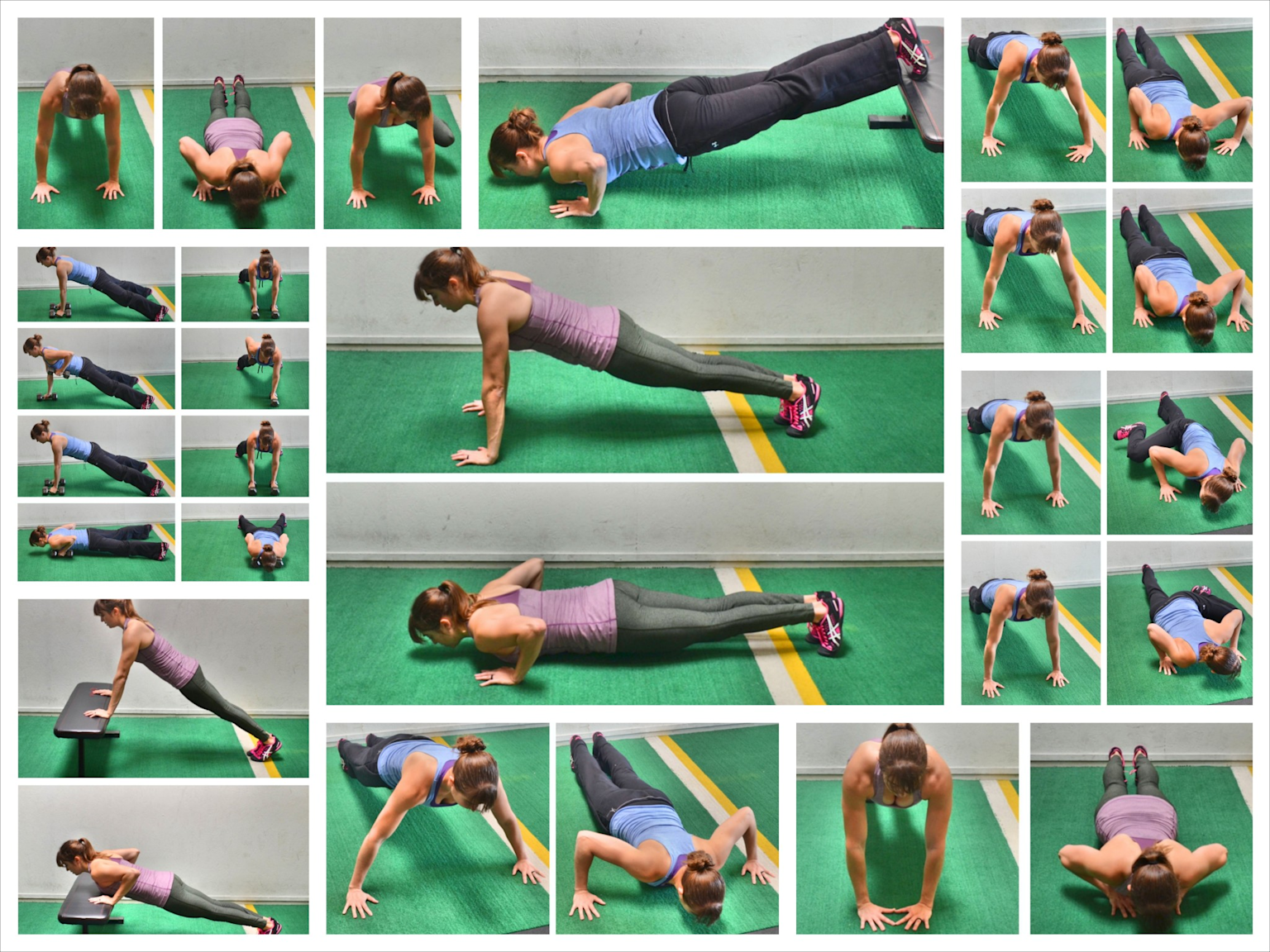

Detailed photo collage showing proper push-up form and variations from multiple angles redefiningstrength
Common progressions include incline push-ups (hands elevated on a stable surface), decline push-ups (feet elevated), and eventually single-arm variations for advanced practitioners. Regression options involve wall push-ups or knee push-ups, though maintaining the plank position through incline variations typically produces superior results.
Squat Mastery: Lower Body Foundation
The bodyweight squat addresses fundamental human movement patterns while building lower body strength, mobility, and stability. Proper execution begins with feet positioned slightly wider than hip-width, toes pointing forward or slightly outward based on individual hip anatomy and mobility restrictions.
Hip initiation proves crucial for proper squat mechanics. Begin the movement by pushing your hips backward as if reaching back to sit in a chair, then allow the knees to bend naturally. This hip-dominant pattern activates the powerful glute muscles while reducing stress on the knee joints.
Depth standards require the hip crease to drop below the knee cap for a full-range squat. This position ensures complete muscle activation while maintaining and improving hip mobility. However, depth should never be achieved by compromising spinal position or knee alignment.
Weight distribution favors the heels while maintaining contact through the entire foot. The knees track in line with the toes throughout the movement, resisting inward collapse that can stress knee ligaments and reduce power output.
The ascent reverses the descent pattern, driving through the heels while maintaining chest elevation and neutral spine position. Focus on spreading the floor apart with your feet—this cue often improves glute activation and overall power output.
Plank Perfection: Core Stability Excellence
The plank exercise develops core stability more effectively than traditional crunches while training the entire kinetic chain in functional patterns. Proper setup involves positioning forearms parallel to each other with elbows directly beneath the shoulders, creating a stable base of support.
Body position forms a straight line from head to heels, with particular attention to maintaining neutral spine curvature. The common error of elevating the hips reduces core engagement and defeats the exercise purpose, while allowing the hips to sag places dangerous stress on the lumbar spine.
Breathing remains controlled and rhythmic throughout the hold. Avoid breath-holding, which elevates blood pressure unnecessarily while reducing oxygen delivery to working muscles. Focus on gentle, continuous breathing while maintaining position stability.
Progressive variations include single-arm planks, side planks for lateral core strength, and dynamic movements like mountain climbers that add cardiovascular challenge while maintaining core stability demands.
Kettlebell Fundamentals: Mastering the Art of Ballistic Training
Beta

Woman demonstrating the correct way to do a kettlebell swing in a fitness tutorial setting youtube
Kettlebell training introduces ballistic movements that develop explosive power, cardiovascular endurance, and functional strength through full-body integration. Unlike traditional weight training that often isolates muscles, kettlebell exercises demand coordination, timing, and neuromuscular efficiency.
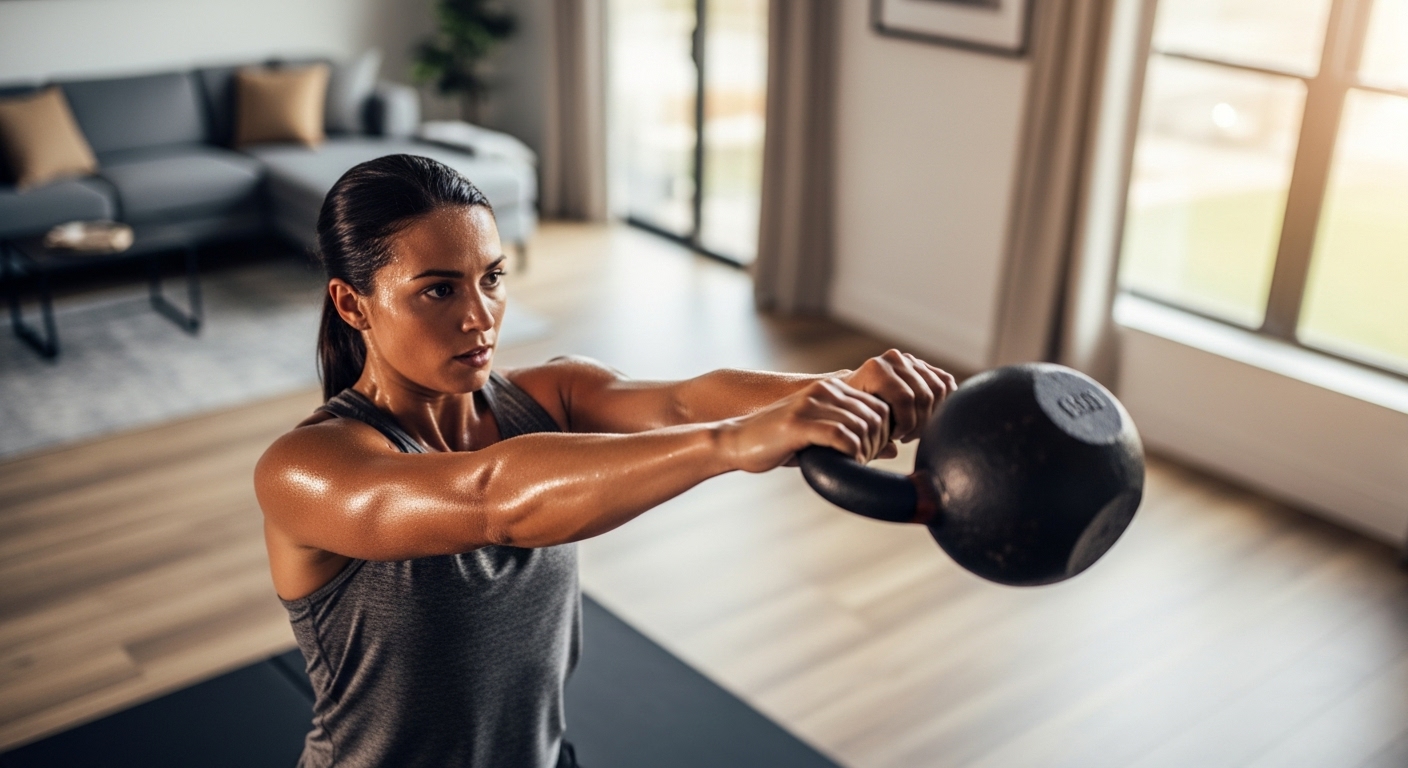
The Kettlebell Swing: Foundation of Power
The kettlebell swing serves as the cornerstone exercise that develops posterior chain strength, explosive hip power, and cardiovascular conditioning simultaneously. This movement primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, and core while providing secondary benefits throughout the entire kinetic chain.
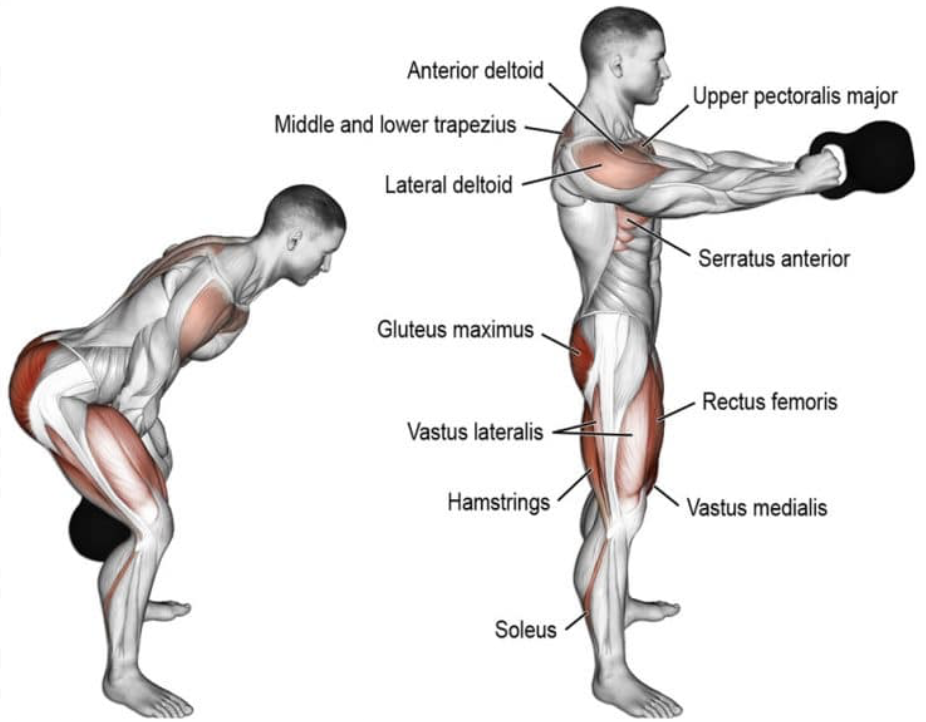
Anatomy of muscle activation during a kettlebell swing exercise highlighting key muscles engaged movemoresitless.wordpress
Setup positioning places the kettlebell approximately 12 inches in front of your feet, which should be positioned slightly wider than shoulder width. Hip hinge mechanics initiate the movement—push your hips backward while maintaining neutral spine alignment, then grasp the kettlebell handle with both hands using an overhand grip.
The hiking motion begins the swing sequence by lifting the kettlebell and immediately pulling it between your legs in a football snap-like motion. This creates the momentum necessary for the explosive hip extension that defines proper swing mechanics.
Power generation occurs through aggressive hip extension—imagine someone pulling your hips forward with a rope attached to your belt buckle. This rapid hip snap, not arm lifting, propels the kettlebell forward and upward to approximately chest height. Your arms remain relatively straight and relaxed, acting merely as connectors between your body and the weight.
The float phase sees the kettlebell momentarily weightless at the top of its trajectory. Resist any urge to lift with your arms or lean backward to increase height—proper hip extension naturally brings the kettlebell to the appropriate level.
Descent control begins as gravity takes over. Allow the kettlebell to fall naturally while preparing to absorb its energy through another hip hinge. The kettlebell should pass close to your body as it swings between your legs, setting up the next explosive repetition.
Common technical errors include squatting instead of hinging at the hips, using arm strength to lift the kettlebell, and allowing excessive forward lean. These mistakes reduce effectiveness while increasing injury risk, particularly to the lower back and shoulders.
Turkish Get-Up: The Ultimate Movement Complex
The Turkish Get-Up represents perhaps the most comprehensive single exercise in existence, combining mobility, stability, strength, and coordination in a complex movement pattern that addresses common deficiencies throughout the kinetic chain.
The seven-phase sequence begins in the supine position with the kettlebell pressed overhead in one arm. Each transition demands precise control and body awareness while maintaining vertical kettlebell position throughout the entire movement.
Phase one involves the initial roll to elbow, using the non-kettlebell arm for support while keeping your eyes focused on the weight overhead. This visual connection helps maintain proper alignment and balance while providing feedback about kettlebell position.
The bridge position (phase two) requires lifting your hips off the ground while supporting body weight on one arm and both feet. This develops extraordinary core strength and shoulder stability while preparing for the leg sweep.
The leg sweep (phase three) involves threading the support leg underneath your body to achieve a kneeling lunge position. This requires significant hip and ankle mobility while maintaining overhead stability and balance.
Standing from the lunge and reversing the entire sequence completes the movement. Each phase should be practiced individually before attempting the complete Turkish Get-Up, allowing for proper motor learning and strength development.
Goblet Squat: Perfect Squatting Mechanics
The goblet squat introduces front-loaded squatting patterns while teaching proper depth, posture, and core engagement. Holding the kettlebell against your chest naturally encourages upright torso position and deeper squat depth compared to bodyweight variations.
Kettlebell positioning involves grasping the handle sides (horns) or cradling the bell portion against your sternum. The weight should rest comfortably against your chest with elbows pointing downward, creating a stable platform that doesn’t interfere with breathing or movement.
Descent mechanics mirror bodyweight squat patterns but with enhanced emphasis on maintaining upright posture due to the front-loaded weight. The kettlebell’s position actually assists in achieving better squat depth by providing counterbalance to your body weight.
At the bottom position, use your elbows to gently push your knees outward, promoting better hip mobility and glute activation. This gentle pressure helps develop the flexibility and strength patterns necessary for deeper, more effective squats.
The ascent emphasizes driving through the heels while maintaining chest elevation and core engagement. The kettlebell’s weight naturally challenges core stability throughout the movement, providing additional training benefits beyond simple leg strengthening.
Designing Your Progressive Training System
Fitness infographic showing a progression chart of six different exercises with numbered steps and sample text on a blue background dreamstime
Effective program design balances progressive overload with adequate recovery while addressing individual needs, limitations, and goals. The most successful approaches utilize periodization principles that systematically vary training stress to optimize adaptations while preventing plateaus and overuse injuries.
Foundation Phase: Movement Mastery (Weeks 1-4)
The initial training phase prioritizes movement quality over intensity, establishing proper exercise technique and building the work capacity necessary for more challenging training phases. This conservative approach prevents injury while creating sustainable habits that support long-term success.
Week 1-2 sessions focus exclusively on bodyweight movements with emphasis on perfect form and controlled tempo. Perform 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions with complete rest between sets, allowing full recovery to maintain movement quality throughout each session.
Basic exercises include bodyweight squats, modified push-ups (knee or incline variations as needed), plank holds, and glute bridges. Add basic kettlebell movements like deadlifts and carries only after demonstrating competency in bodyweight patterns.
Week 3-4 introduces simple circuit training, alternating between two exercises with minimal rest. For example, 30 seconds of squats followed immediately by 30 seconds of modified push-ups, then 90 seconds of complete rest. This develops the work capacity needed for more advanced training while maintaining movement quality focus.
Progressive overload occurs through increased repetitions, longer work periods, or reduced rest intervals rather than added exercise complexity. This methodical approach builds a solid foundation while minimizing injury risk during this crucial learning phase.
Strength Development Phase: Building Power (Weeks 5-8)
After establishing movement competency, the strength phase introduces higher loads and more complex exercises while maintaining emphasis on proper technique and progressive overload.
Kettlebell swings become the cornerstone exercise, starting with light weights and perfect form before progressing to heavier loads and higher repetitions. Begin with 10-15 swings per set, focusing on explosive hip extension and proper breathing patterns.
Goblet squats replace bodyweight squats, introducing front-loaded resistance that challenges stability and strength simultaneously. Start with lighter weights that allow perfect form throughout the full range of motion before progressing to heavier loads.
Complex training pairs complement this phase effectively. Following a strength exercise like goblet squats immediately with an explosive bodyweight movement like jump squats enhances power development through post-activation potentiation.
Training frequency increases to 3-4 sessions per week, with at least one full rest day between intense sessions. This allows adequate recovery while maintaining training momentum and skill development.
Power Integration Phase: Athletic Performance (Weeks 9-12)
The final phase integrates all previously learned movements while emphasizing power development, metabolic conditioning, and advanced exercise variations that challenge multiple systems simultaneously.
Turkish Get-Ups enter the program during this phase, starting with bodyweight versions before progressing to loaded variations. This exercise develops the integration and stability that ties all other movements together while addressing any remaining movement deficiencies.
High-intensity circuit training becomes the primary conditioning method, combining strength and cardiovascular challenges in time-efficient protocols. Example circuits might alternate between kettlebell swings, bodyweight squats, push-ups, and carries with work-to-rest ratios favoring incomplete recovery.
Advanced bodyweight progressions like single-leg squats, archer push-ups, and dynamic plank variations provide continued challenge and development opportunities for practitioners ready to progress beyond basic movements.
Sample Workouts: From Beginner to Elite

Illustration showing beginner, intermediate, and advanced fitness levels with corresponding body progressions youtube
Practical application transforms theoretical knowledge into measurable results. These scientifically designed workouts provide immediate implementation strategies while demonstrating progression principles and proper exercise integration.
Beginner Workout: Movement Foundation Builder
Warm-Up Sequence (5 minutes)
- Joint mobility circles: 5 rotations each direction for ankles, knees, hips, shoulders
- Arm swings: 10 forward and backward
- Bodyweight squats: 10 slow, controlled repetitions
- Wall push-ups: 10 repetitions focusing on full range of motion
Main Training Block (18-22 minutes)
Circuit A – Perform 3 rounds with 90 seconds rest between rounds:
- Bodyweight squats: 30 seconds (focus on depth and control, rest as needed)
- Modified push-ups: 30 seconds (knee or incline version maintaining plank position)
- Plank hold: 20-30 seconds (maintain perfect alignment, breathe normally)
- Active rest: 30 seconds (gentle walking or light stretching)
Circuit B – Perform 2 rounds with 2 minutes rest between rounds:
- Kettlebell deadlift: 8-10 repetitions (focus on hip hinge pattern, light weight)
- Glute bridges: 12-15 repetitions (squeeze glutes at top, control descent)
- Standing marches: 20 total repetitions (10 each leg, focus on balance)
Recovery and Mobility (5 minutes)
- Standing forward fold: 60 seconds (gentle stretch, don’t force depth)
- Seated spinal twist: 30 seconds each direction
- Child’s pose: 90 seconds (focus on breathing and relaxation)
This workout prioritizes learning over intensity. Rest as needed to maintain perfect form, and modify exercises if they become too challenging. Success is measured by movement quality, not speed or difficulty.
Intermediate Workout: Strength and Power Integration
Dynamic Warm-Up (8 minutes)
- Leg swings: 10 forward/back and side-to-side each leg
- Hip circles: 8 each direction
- Arm circles and shoulder rolls: 10 each direction
- Bodyweight squats with overhead reach: 10 repetitions
- Push-up to downward dog: 8 repetitions
Main Training Session (28-32 minutes)
Strength Superset A – 4 rounds, 75 seconds rest:
- Goblet squats: 10-12 repetitions (focus on depth and control)
- Push-up variations: 8-10 repetitions (diamond, wide, or standard based on ability)
Power Complex B – 3 rounds, 2 minutes rest:
- Kettlebell swings: 20 repetitions (explosive hip extension, chest-high float)
- Jump squats: 8-10 repetitions (land softly, immediate transition to next swing set)
Metabolic Circuit C – 3 rounds, 90 seconds rest:
- Turkish Get-Up practice: 3 each side (bodyweight or light kettlebell)
- Plank to downward dog: 30 seconds
- High knees: 30 seconds
- Mountain climbers: 30 seconds
Active Recovery (5 minutes)
- Light walking with deep breathing
- Gentle stretching focusing on hips, shoulders, and spine
- Foam rolling if available
This intermediate protocol balances strength development with power training while introducing more complex movements and higher training densities.
Advanced Workout: Elite Performance Protocol
Movement Preparation (10 minutes)
- Dynamic flow combining multiple movement patterns
- Activation exercises targeting individual weaknesses
- Practice rounds of complex movements at reduced intensity
- Joint-specific mobility work based on assessment findings
High-Intensity Training Block (35-40 minutes)
Strength Block – 5 rounds, 3 minutes rest:
- Turkish Get-Up: 2-3 repetitions each side (moderate to heavy kettlebell)
- Single-arm push-up progression: Maximum quality repetitions each side
- Pistol squat progression: 3-5 repetitions each leg (assisted or full based on ability)
Power Development Block – 4 rounds, 2 minutes rest:
- Kettlebell snatch: 5 repetitions each arm (explosive hip and shoulder action)
- Clapping push-ups: 5-8 repetitions (maximum explosive output)
- Single-leg bounds: 6 each leg (focus on distance and landing control)
Conditioning Finisher – 4 rounds, 60 seconds rest:
- Kettlebell swing intervals: 30 seconds maximum effort/15 seconds transition
- Burpee variations: 30 seconds (chest-to-ground, explosive jump)
- Mountain climber variations: 30 seconds (cross-body, speed, or single-arm)
Advanced practitioners often benefit from consulting resources from the National Strength and Conditioning Association for cutting-edge training methodologies and continuing education opportunities.
Advanced Techniques: Mastering Complex Movement Patterns

Woman exercising with creative fitness illustrations symbolizing energy and strength freepik
Advanced training techniques separate recreational exercisers from serious athletes by demanding exceptional coordination, strength, and movement mastery while providing unparalleled benefits in power development, injury prevention, and functional capacity.
Unilateral Training: Correcting Imbalances and Building Real-World Strength
Single-limb exercises expose and correct the asymmetries that bilateral movements often conceal. Most individuals develop subtle imbalances through daily activities, sports participation, and movement preferences that can limit performance and increase injury risk over time.
The single-arm kettlebell swing challenges anti-rotation core strength while developing unilateral hip power and shoulder stability. Begin with significantly lighter weights than bilateral swings, as the offset loading dramatically increases stability demands throughout the kinetic chain.
Proper execution requires maintaining perfect spinal alignment while resisting rotation forces created by the off-center load. The non-working arm can initially extend to the side for counterbalance, though advanced practitioners keep it at their side to increase the stability challenge.
Single-leg deadlifts using bodyweight develop posterior chain strength, balance, and proprioception simultaneously. The key lies in maintaining hip hinge mechanics while standing on one leg, creating enormous stability and strength demands throughout the supporting leg and core musculature.
Archer push-ups bridge the gap between standard push-ups and the elite one-arm push-up by teaching asymmetrical loading patterns. Shift your weight toward one arm while the other provides minimal assistance, gradually reducing the assistance until single-arm execution becomes possible.
Complex and Combination Movements
Complex movements combine multiple exercises into flowing sequences that challenge coordination, strength, and cardiovascular systems simultaneously while providing maximum training efficiency for time-pressed individuals.
The kettlebell flow might combine deadlifts, swings, cleans, presses, and squats in continuous sequence without setting the weight down. Each movement flows naturally into the next, creating unbroken chains of exercises that challenge multiple energy systems and movement patterns.
Bodyweight complexes connect exercises like burpees, mountain climbers, and push-ups into seamless sequences that resemble martial arts forms or gymnastics routines. Advanced practitioners create elaborate movement chains that develop both physical capacity and movement artistry.
Effective complex design requires logical exercise progression and smooth transitions. Movements should complement each other rather than creating awkward position changes that interrupt flow and reduce training effectiveness.
Turkish Get-Up variations represent the ultimate complex movement, combining every fundamental movement pattern into a single, flowing exercise that develops mobility, stability, strength, and coordination simultaneously.
High-Intensity Metabolic Protocols
Advanced metabolic conditioning creates massive caloric expenditure while improving cardiovascular fitness, muscular endurance, and mental toughness through protocols that push the boundaries of comfortable exercise.
Tabata intervals (20 seconds maximum effort, 10 seconds rest, repeated for 8 rounds) work exceptionally well with kettlebell swings, burpees, or other high-intensity exercises. The brief work periods allow for maximum intensity while short rests prevent complete recovery, creating enormous metabolic stress and adaptation.
EMOM (Every Minute On the Minute) protocols provide consistent work-to-rest ratios while allowing natural intensity regulation. Perform a prescribed number of repetitions at the start of each minute, using remaining time for recovery. As fitness improves, increase repetitions or add exercises to reduce rest periods.
Density circuits challenge your ability to maintain work output over extended periods. Complete as many rounds as possible of a given circuit within a set timeframe, resting only as needed to maintain movement quality. Track total rounds completed and aim for improvement in subsequent sessions.
Nutrition and Recovery: Optimizing Your Results

Post workout meals including salmon, egg scramble, trail mix, hummus, and cottage cheese with fruits provide protein to repair tissues and build muscle within 2 hours after exercise shutterstock
Training represents only one component of the fitness equation. Proper nutrition, strategic recovery, and lifestyle optimization often determine whether training adaptations occur optimally or progress stagnates despite consistent effort.
Fueling High-Intensity Training
Pre-workout nutrition should provide readily available energy without causing digestive distress during explosive movements. Consume a light meal containing both carbohydrates and easily digestible protein 1-2 hours before training. Effective options include oatmeal with berries and a small amount of protein powder, banana with almond butter, or Greek yogurt with honey.
For early morning sessions, many individuals train successfully in a fasted state, particularly for sessions lasting less than 45 minutes. However, kettlebell training’s high-intensity nature may benefit from some fuel, even if minimal. A piece of fruit or small amount of easily digestible carbohydrates often improves performance without causing digestive issues.

Variety of healthy post-workout meals showcasing balanced nutrition for muscle recovery foodforfitness.co
Post-workout nutrition becomes crucial for recovery and adaptation, particularly after high-intensity kettlebell and bodyweight sessions. While the “anabolic window” isn’t as narrow as once believed, consuming protein within 2-3 hours post-exercise optimizes muscle protein synthesis and recovery processes.
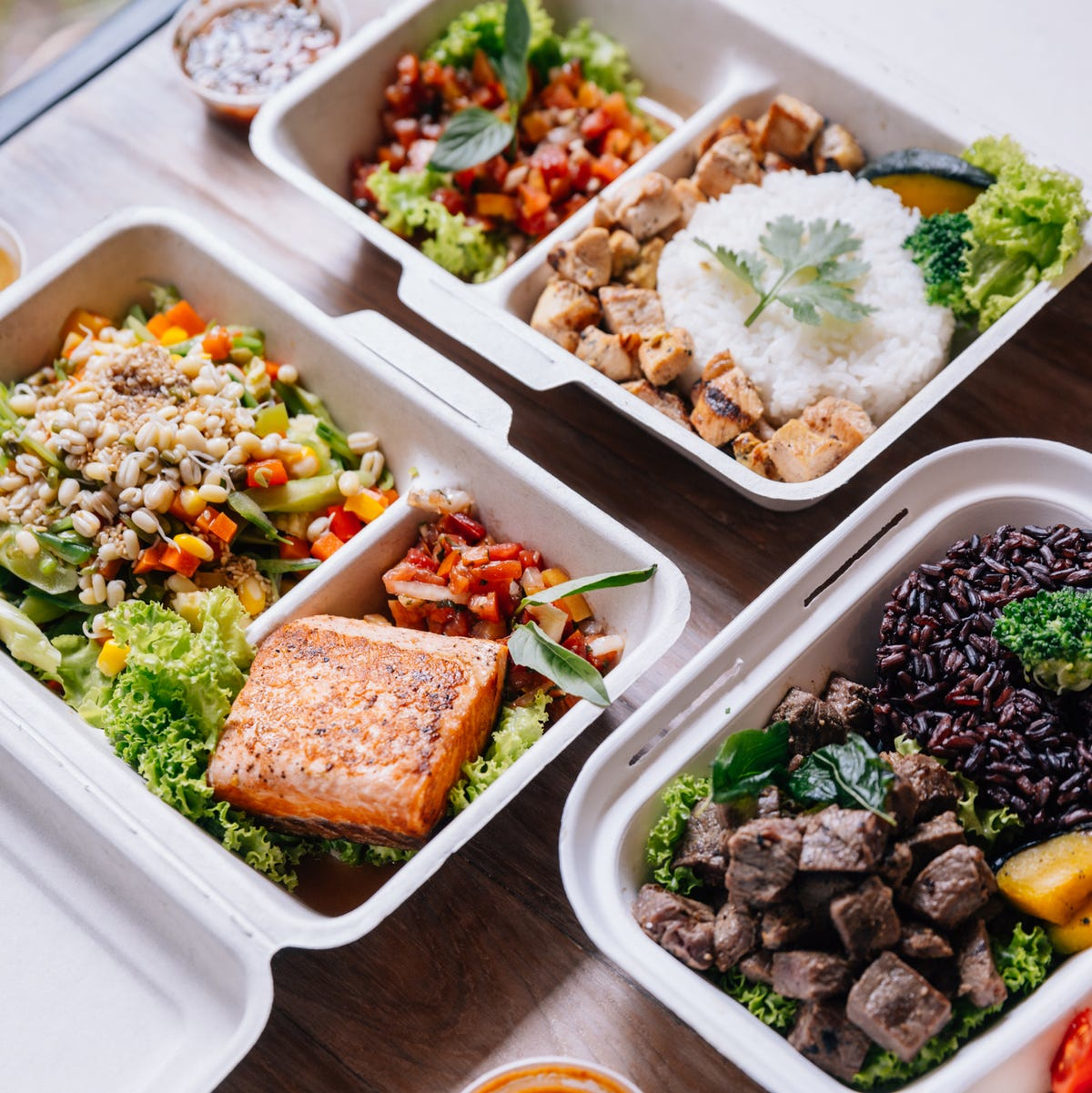

Balanced meal prep containers with protein-rich foods like grilled salmon, chicken, beef, rice, and vegetables for post-workout nutrition and muscle recovery menshealth
Aim for 20-25 grams of high-quality protein paired with carbohydrates to replenish muscle glycogen stores. Effective combinations include chocolate milk, protein smoothies with fruit, or whole food meals combining lean protein with complex carbohydrates.
Hydration significantly impacts both performance and recovery. Begin each workout adequately hydrated and replace fluids lost through sweating. Monitor urine color as a simple hydration assessment—pale yellow indicates adequate hydration while dark yellow suggests fluid deficit requiring attention.
Recovery Strategies for Continued Progress
Recovery encompasses far more than rest days from exercise. Sleep optimization, stress management, and active recovery all contribute to your body’s ability to adapt to training stress and continue progressing toward goals.
Sleep represents the most underappreciated component of fitness success. During deep sleep phases, growth hormone release peaks, protein synthesis accelerates, and motor learning consolidates—including the complex movement patterns learned during kettlebell and bodyweight training sessions.
Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly, maintaining consistent sleep and wake times even on weekends. Sleep environment optimization includes cool temperatures (65-68°F), complete darkness, and minimal noise disruption. Consider blackout curtains, white noise machines, or sleep masks if environmental control proves challenging.
Active recovery days promote blood flow and nutrient delivery to recovering muscles without adding significant training stress. Light walking, gentle cycling, or swimming provides movement without intensity. Yoga or tai chi offer excellent active recovery options while addressing flexibility and stress reduction simultaneously.
Stress management directly impacts recovery through its effects on cortisol levels and sleep quality. Chronic stress impairs recovery, increases injury risk, and can sabotage even perfectly designed training programs. Implement stress reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or regular nature exposure to build resilience and improve recovery capacity.
Strategic Supplementation for Enhanced Performance
While proper nutrition forms the foundation of optimal performance, certain supplements can enhance recovery and training adaptations when used appropriately. However, supplements cannot compensate for poor diet, inadequate sleep, or inconsistent training practices.
Creatine monohydrate stands as the most researched and effective supplement for power-based activities like kettlebell training. Benefits include increased power output, improved recovery between sets, enhanced training volume capacity, and increased muscle cell hydration. Take 3-5 grams daily; timing proves less important than consistency.
Protein supplementation offers convenience for meeting daily protein requirements, particularly beneficial for individuals with higher needs or challenging schedules. Whey protein provides rapid absorption, making it ideal post-workout, while casein protein’s slower digestion makes it suitable before bed for overnight recovery support.
Omega-3 fatty acids support recovery through anti-inflammatory effects while providing cardiovascular and cognitive benefits. If fatty fish intake is limited, high-quality fish oil supplements can bridge nutritional gaps, though whole food sources remain preferable when accessible.
The supplement industry contains many ineffective products with exaggerated claims. Focus on proven fundamentals rather than chasing trends, and remember that supplements should enhance, not replace, solid nutrition practices.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges

Wooden blocks arranged as steps with an ascending arrow and rocket leading to a target symbolizing achievement and progress dreamstime
Progress rarely follows a linear path, and understanding how to navigate common obstacles separates those who achieve long-term success from those who abandon their goals when challenges arise.
Breaking Through Performance Plateaus
Plateaus represent normal adaptation responses where your body has successfully adjusted to current training demands. This adaptation actually demonstrates progress—your fitness level has improved to the point where previous challenges no longer provide adequate stimulus for continued development.
The solution involves strategically modifying training variables to provide novel challenges. If you’ve emphasized strength development with longer rest periods and heavier loads, switching to metabolic conditioning with shorter rests and higher repetitions can reignite progress while addressing different fitness components.
Deload weeks—planned periods of reduced training volume and intensity—often precede breakthrough periods. These strategic recovery phases allow accumulated fatigue to dissipate while giving your nervous system time to consolidate learned movement patterns and prepare for higher training loads.
Exercise variation provides another plateau-busting strategy. If standard kettlebell swings have become routine, progress to single-arm variations, different swing styles, or entirely different exercises that challenge your body in novel ways while preventing training monotony.
Periodization—systematic variation in training focus over time—prevents adaptation plateaus by ensuring your body faces constantly evolving challenges. Alternate between strength-focused phases, power development periods, and conditioning emphases to maintain continuous adaptation.
Overcoming Mental Barriers and Motivation Challenges
Physical plateaus often have psychological components that must be addressed for continued progress. Fear of failure, perfectionist tendencies, or negative self-comparison can create mental blocks that limit progress despite physical capability.
Imposter syndrome frequently affects intermediate trainees who feel they don’t deserve to be in advanced fitness discussions or attempt challenging exercises. These feelings are normal and temporary—everyone starts as a beginner, and progress comes through persistent effort rather than natural talent or genetic gifts.
Setting process goals rather than outcome goals maintains motivation during challenging periods. Instead of focusing solely on achieving specific performance milestones (outcome), concentrate on improving movement quality, training consistency, or effort level (process). Process goals remain within your direct control while outcome goals depend partly on factors beyond your influence.
Visualization techniques, commonly employed by elite athletes, can accelerate skill development and build confidence. Spend several minutes daily mentally rehearsing perfect exercise technique or visualizing successful workout completion. This mental practice strengthens neural pathways associated with skilled movement execution.
Social support significantly impacts long-term adherence. Share your fitness journey with family, friends, or online communities that provide encouragement, accountability, and shared experiences. Having others invested in your success creates additional motivation during challenging periods.
Injury Prevention and Management Strategies
Minor aches and pains are inevitable in any serious fitness journey, but distinguishing between normal adaptation discomfort and potential injury signals proves crucial for long-term success and health.
Sharp, sudden pain requires immediate attention and possible professional evaluation. Dull, general muscle soreness typically indicates normal adaptation processes and responds well to active recovery, gentle movement, and adequate nutrition.
Movement screening can identify potential problem areas before they become injuries. Simple assessments like overhead squats, single-leg stands, or shoulder mobility tests reveal limitations that could lead to compensatory movement patterns and eventual tissue breakdown.
When minor injuries occur, early intervention prevents small issues from becoming major problems. The PRICE protocol (Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) remains appropriate for acute injuries, while gradual return to activity under professional guidance ensures proper healing without re-injury.
Working with qualified healthcare providers—physical therapists, sports medicine physicians, or certified trainers—can accelerate recovery while teaching injury prevention strategies. These professionals identify movement dysfunctions and provide corrective exercises that address root causes rather than merely treating symptoms.
Building Sustainable Long-Term Success

Fitness and gym training infographic showing workout types, equipment, calories burned, and exercise examples freepik
Sustainable fitness success requires more than effective workouts—it demands lifestyle integration, realistic goal setting, and strategies for maintaining motivation through inevitable life challenges and changing circumstances.
Creating Unbreakable Habits
The most effective fitness program remains the one you’ll follow consistently over months and years. Elaborate routines requiring perfect conditions or significant time commitments often fail when life becomes complicated or motivation temporarily wanes.
Start with minimum effective doses—the smallest amount of exercise that produces meaningful results. This might mean 15-minute sessions three times weekly rather than hour-long workouts that become overwhelming. Success with smaller commitments builds confidence and creates habits that naturally expand over time.
Habit stacking involves linking new fitness behaviors to existing daily routines, creating automatic triggers that reduce the mental energy required for exercise initiation. Performing bodyweight squats while morning coffee brews or completing a plank hold during evening news creates seamless integration into established patterns.
Environmental design supports habit formation by removing barriers and creating visual cues for desired behaviors. Keeping your kettlebell visible in living spaces serves as a constant reminder while having workout clothes readily available eliminates friction that might prevent training sessions.
Identity-based habit formation proves more powerful than outcome-based approaches. Instead of saying “I want to lose weight,” adopt the identity “I am someone who exercises regularly.” This subtle shift makes decisions easier—people who see themselves as athletic naturally make choices that support that identity.
Adapting to Life’s Inevitable Changes
Life circumstances constantly evolve—career changes, relationship developments, family additions, and other major transitions can disrupt even well-established fitness routines. Building adaptability into your approach ensures continued progress despite changing circumstances.
Travel frequently disrupts established routines, but bodyweight exercises require no equipment and minimal space. Master a core set of bodyweight movements that can be performed anywhere—hotel rooms, outdoor spaces, or small apartments. This ensures training consistency regardless of location or circumstances.
Time constraints serve as common exercise barriers, but effective workouts can be completed in remarkably short timeframes. High-intensity circuit training provides significant benefits in 10-15 minutes when performed consistently, making time scarcity less of a limiting factor.
Seasonal motivation variations are normal and predictable. Many people struggle with consistency during darker winter months while finding outdoor activities more appealing during summer. Plan for these variations by having indoor and outdoor options available, preventing weather or seasonal changes from derailing progress.
Equipment limitations need not halt progress. If your kettlebell becomes unavailable, bodyweight exercises maintain fitness and movement patterns until normal training resumes. Adaptability prevents perfectionist thinking that creates all-or-nothing approaches to fitness.
Long-Term Vision and Legacy Thinking
Elite athletes use periodization—systematic variation in training focus over extended periods—to peak for important competitions while avoiding overtraining and burnout. This same principle applies to recreational fitness enthusiasts seeking long-term progress and enjoyment.
Annual planning might include phases focused on strength development during winter months, conditioning emphasis during spring preparation, skill acquisition during summer activities, and recovery focus during autumn transitions. This systematic variation prevents boredom while addressing different fitness components throughout the year.
Goal evolution represents healthy progress rather than inconsistency or lack of focus. As fitness improves and interests develop, goals should adapt accordingly. Someone beginning with basic health goals might progress to strength development, then athletic performance, then movement quality mastery as they advance through their fitness journey.
Legacy thinking involves considering how current fitness investments will benefit future decades. The strength, bone density, balance, and movement competency developed through consistent training provide protection against age-related decline while maintaining independence and quality of life for years to come.
Building fitness habits in your 20s, 30s, or 40s creates dividends that compound over decades, making the difference between vibrant aging and gradual decline. According to research from the Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, individuals who maintain regular exercise throughout middle age show dramatically better physical and cognitive function in their 70s and 80s.
Conclusion: Your Transformation Starts Today

A group of people stacking their hands together in a gesture of teamwork and fitness motivation dreamstime
The combination of bodyweight exercises and kettlebell training represents far more than a convenient workout solution—it embodies a philosophy of movement that emphasizes functionality, efficiency, and sustainable progress throughout life. This guide has provided you with the scientific knowledge, practical tools, and strategic insights necessary to build exceptional fitness using minimal equipment and maximum intelligence.
Your fitness journey is uniquely personal, shaped by individual goals, constraints, preferences, and circumstances. However, the fundamental principles explored throughout this guide—progressive overload, movement quality, recovery optimization, and consistent application—remain universal truths that apply regardless of your starting point or ultimate destination.
The remarkable versatility of this training approach ensures continued relevance as your fitness level and goals evolve. The same exercises that challenge complete beginners can be modified and progressed to test elite athletes, making your investment in learning these movements valuable for decades to come. Whether you’re pursuing basic health improvements, athletic performance, or movement mastery, these tools adapt to serve your changing needs.
Remember that mastery emerges through patient, persistent practice rather than seeking shortcuts or complex solutions. Focus on executing fundamental movements with precision and gradually building upon this foundation as competency develops. The individual who masters basic patterns and applies them consistently will always achieve superior results compared to someone who knows advanced techniques but applies them sporadically.
Success in fitness, as in life, comes from making small, consistent choices that compound over time. Every workout completed, every healthy choice made, and every moment invested in building a stronger body creates positive momentum that extends far beyond physical appearance to encompass confidence, resilience, energy, and life satisfaction.
Your transformation begins with the decision to start, continues through consistent action, and culminates in a lifestyle that supports lifelong health and vitality. The tools are in your hands, the knowledge is in your mind, and the power to change lies within your daily choices.
Take the first step today. Your future self will thank you for every movement, every challenge embraced, and every day you chose progress over comfort. The journey to exceptional fitness begins now—make it count.

Jodie Carter is a REPS Level 3 certified personal trainer with over 8 years of experience in strength training and home gym design. She holds qualifications in exercise physiology and has helped over 500 clients design effective home workout spaces. Jodie regularly contributes to UK fitness publications and maintains continuing education in the latest exercise science research.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links to products I personally use and recommend. When you purchase through these links, I may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. All recommendations are based on my genuine experience and testing—I only recommend products I actually use in my own home.













